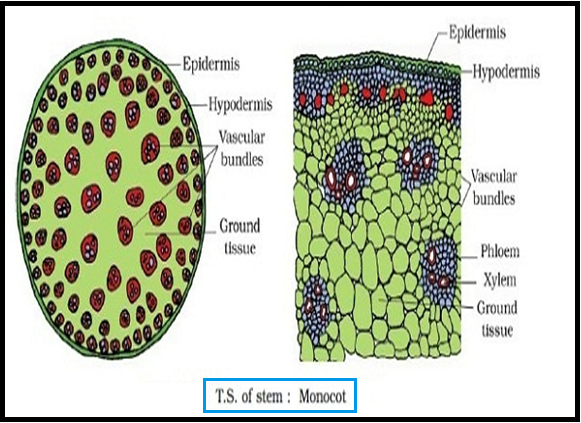
DICOTYLEDONOUS STEM
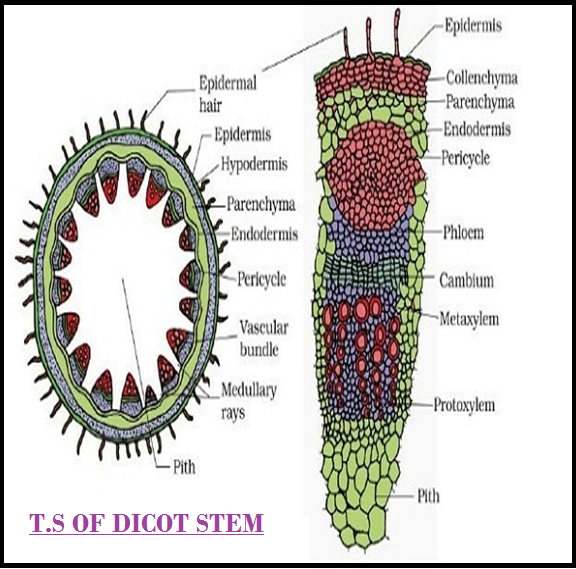
● The`color{violet}(" transverse section")` of a typical `color{violet}("young dicotyledonous stem")` shows that the `color{brown}("epidermis")` is the outermost protective layer of the `color{violet}("stem.")`
● Covered with a thin layer of cuticle, it may `color{violet}("bear trichomes")` and a `color{violet}("few stomata.")`
● The `color{violet}("cells")` arranged in multiple layers between `color{violet}("epidermis")` and `color{violet}("pericycle constitute")` the cortex.
● It consists of `color{violet}("three sub-zones.")`
● The outer `color{brown}("hypodermis,")` consists of a few layers of `color{violet}("collenchymatous cells")` just below the epidermis, which provide mechanical strength to the `color{violet}("young stem. ")`
● `color{brown}("Cortical layers")` below `color{violet}("hypodermis")` consist of rounded `color{violet}("thin walled parenchymatous cells")` with conspicuous intercellular spaces.
● The innermost layer of the `color{violet}("cortex")` is called the `color{brown}("endodermis.")`
● The `color{violet}("cells of the endodermis")` are rich in `color{violet}("starch grains")` and the layer is also referred to as the `color{brown}("starch sheath.")`
● `color{brown}("Pericycle")` is present on the inner side of the `color{violet}("endodermis")` and above the `color{violet}("phloem")` in the form of semi-lunar patches of `color{violet}("sclerenchyma.")`
● In between the `color{violet}("vascular bundles")` there are a few layers of radially placed `color{violet}("parenchymatous cells,")` which constitute medullary rays.
● A large number of `color{brown}("vascular bundles")` are arranged in a ring ; the ‘ring’ arrangement of `color{violet}("vascular bundles ")` is a characteristic of `color{violet}("dicot stem.")`
● Each `color{violet}("vascular bundle")` is `color{violet}("conjoint,")` open, and with `color{violet}("endarch protoxylem.")`
● A large number of rounded, `color{violet}("parenchymatous cells")` with large intercellular spaces which occupy the central portion of the `color{violet}("stem constitute")` the `color{brown}("pith.")`
● Covered with a thin layer of cuticle, it may `color{violet}("bear trichomes")` and a `color{violet}("few stomata.")`
● The `color{violet}("cells")` arranged in multiple layers between `color{violet}("epidermis")` and `color{violet}("pericycle constitute")` the cortex.
● It consists of `color{violet}("three sub-zones.")`
● The outer `color{brown}("hypodermis,")` consists of a few layers of `color{violet}("collenchymatous cells")` just below the epidermis, which provide mechanical strength to the `color{violet}("young stem. ")`
● `color{brown}("Cortical layers")` below `color{violet}("hypodermis")` consist of rounded `color{violet}("thin walled parenchymatous cells")` with conspicuous intercellular spaces.
● The innermost layer of the `color{violet}("cortex")` is called the `color{brown}("endodermis.")`
● The `color{violet}("cells of the endodermis")` are rich in `color{violet}("starch grains")` and the layer is also referred to as the `color{brown}("starch sheath.")`
● `color{brown}("Pericycle")` is present on the inner side of the `color{violet}("endodermis")` and above the `color{violet}("phloem")` in the form of semi-lunar patches of `color{violet}("sclerenchyma.")`
● In between the `color{violet}("vascular bundles")` there are a few layers of radially placed `color{violet}("parenchymatous cells,")` which constitute medullary rays.
● A large number of `color{brown}("vascular bundles")` are arranged in a ring ; the ‘ring’ arrangement of `color{violet}("vascular bundles ")` is a characteristic of `color{violet}("dicot stem.")`
● Each `color{violet}("vascular bundle")` is `color{violet}("conjoint,")` open, and with `color{violet}("endarch protoxylem.")`
● A large number of rounded, `color{violet}("parenchymatous cells")` with large intercellular spaces which occupy the central portion of the `color{violet}("stem constitute")` the `color{brown}("pith.")`